Family offices have quietly become one of the most influential capital allocators in the global investment ecosystem. From managing generational wealth to backing alternative investments like AIFs, private equity, and pre-IPO opportunities, family offices today operate more like institutional investors than traditional wealth managers.
What Is a Family Office?
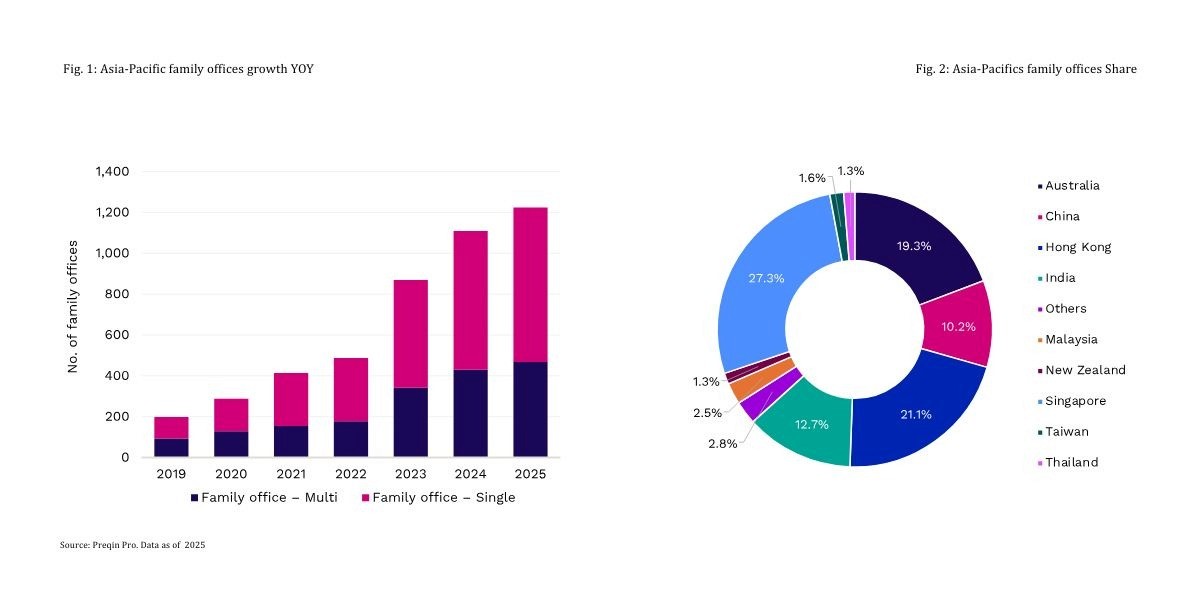
A family office is a private organisation set up to manage the wealth, investments, and long-term financial affairs of a high-net-worth or ultra-high-net-worth family. As per 2025, the number of family offices will grow significantly from double digit to 300+ as compared 2020 to 2025.
Unlike traditional wealth management, family offices focus on:
Capital preservation across generations
Strategic asset allocation
Direct investments and alternatives
Governance, succession, and legacy planning
Family Office vs Traditional Wealth Management
Aspect | Family Office | Traditional Wealth Management |
Client Base | Single family or few families | Multiple unrelated clients |
Investment Approach | Highly customised | Semi-standardised products |
Asset Classes | Direct equity, AIFs, PE, real assets | Mutual funds, PMS, listed equity |
Decision Control | Family-driven | Advisor-driven |
Time Horizon | Multi-generational | Short to medium term |
Types of Family Offices
Single-Family Office (SFO)
Established by one ultra-wealthy family to manage its entire financial ecosystem.
Full control and confidentiality
High operating cost
Suitable for UHNI families
Multi-Family Office (MFO)
Serves multiple families under a shared platform.
Cost-efficient
Access to institutional-grade opportunities
Growing rapidly in India
Family Office Trends: India vs Asia vs World
Region | Key Trends |
India | Rapid rise of first-generation family offices, strong AIF adoption, focus on SME & Pre-IPO |
Asia (ex-India) | Structured family offices, strong PE & VC exposure, global diversification |
Global | Mature governance, high allocation to alternatives, co-investments with institutions |
India stands out for its faster transition from traditional wealth to structured alternative investing, especially via AIFs.
Family Office Investment Focus Areas
Modern family offices typically allocate across:
Listed equity (domestic & global)
Private equity and venture capital
Real assets (real estate, infrastructure)
Pre-IPO and unlisted equity
Among these, AIFs have emerged as a preferred vehicle due to structure, regulation, and access
2. Asset Allocation Shift (YoY %) – India vs World
Allocation to Alternative Assets (AIFs, PE, VC, Private Credit)
Year | India – Alternatives % | Global – Alternatives % |
2020 | 28% | 38% |
2021 | 32% | 40% |
2022 | 36% | 42% |
2023 | 41% | 44% |
2024 | 45% | 46% |
2026E | 50%+ | 48–50% |
Role of AIFs in the Next Phase of Family Office Growth
AIFs are no longer “alternative” for family offices. They are becoming core portfolio components, particularly for:
Risk-adjusted alpha generation
Access to India’s private growth economy
Professionalised deal execution
Time-efficient diversification
For Indian family offices, AIFs bridge the gap between direct investing and traditional markets.
To know more about Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) in India [Click here]
How to invest in an AIF? Minimum capital required and key advantages [Click here]
For Venture Capital (VC) funds [Click here]











